Generative AI has the ability to create new content, moving beyond traditional AI’s data analysis and improved forecasting capabilities. It is the latest and, perhaps, the most important step so far in the technology’s evolution, preceded by traditional AI systems, machine learning, deep learning1, neural networks, and automated speech recognition and language processing.
In the past, traditional AI has been helpful in predicting outcomes and focusing on a narrow task, such as accurately identifying and categorizing images. Generative AI, on the other hand, is based on a text prompt, whereby a user types text-based inputs in the form of a question or request and the large language model2 does its best to produce an appropriate response. It offers broader applications, using deep learning techniques and large language models to generate unique and new content using trained data.
Large addressable market
According to Bloomberg and the International Development Corporation (IDC), the overall market for generative AI could grow at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 45%, from $14 billion in 2020 to $1.30 trillion in 2032. The rapid growth in generative AI is expected to support demand for semiconductor chips, software, networking, and memory storage solutions.
Generative AI market 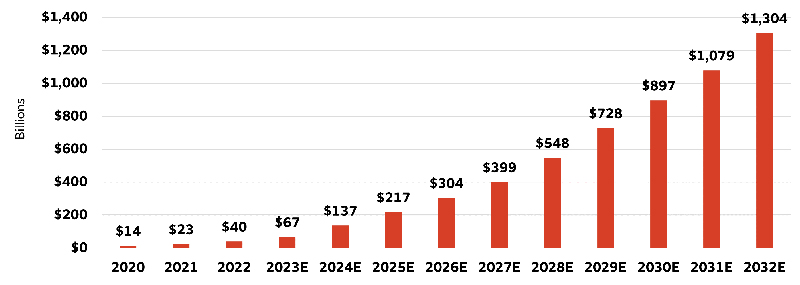
Sources: Wells Fargo Investment Institute, Bloomberg, and IDC. Data as of June 1, 2023. E = estimated. Estimates based on Bloomberg Intelligence forecasts using IDC data for the overall generative AI market.
Major computing platform shift underway
AI has been around since the 1950s and has experienced several false starts along the way. However, over the past two decades, the convergence of big data, advances in high-performance computing power, advances in machine learning algorithms, and cloud computing were instrumental in driving recent advancements in AI. In terms of size and importance, it is widely believed that generative AI represents the next major computing platform shift upon which various types of software and new applications will be built.
Mainstream adoption — ChatGPT
ChatGPT was created by OpenAI, an AI research organization founded by various entrepreneurs and researchers in December 2015. The mainstream adoption of generative-AI-based large language models has taken off, particularly in the case of ChatGPT. The application reached 100 million active users in two months after its introduction in November 2022. Although downloads of ChatGPT started to show some signs of moderating by June 2023, ChatGPT represents one of the fastest-growing consumer applications in history.
1 Deep learning refers to a type of AI that uses layers of neural networks to mimic how humans learn.
2 A large language model is a deep-learning neural network that is trained on massive amounts of existing text to generate new text similar to human language.
Generative AI’s two most visible macroeconomic issues are its impact on labor productivity and the job market. Beyond that is the direct, more immediate impact on economic growth from business investment in AI-related technology equipment and software. A recent McKinsey & Company (McKinsey) study estimated that generative AI could add 0.1% – 0.6% to the global economy’s average annual productivity growth between now and 2040, depending on the speed with which the technology is absorbed and workers’ time savings are realized.3
Sector implications of AI
The most obvious AI beneficiaries are the companies at the forefront of developing and adopting these technologies as well as those that are supplying the necessary components. Many of these companies are constituents of the Information Technology, Consumer Discretionary, and Communication Services sectors, which together account for 47% of the S&P 500 Index (as of September 21, 2023).
S&P 500 Index is heavily weighted toward AI plays 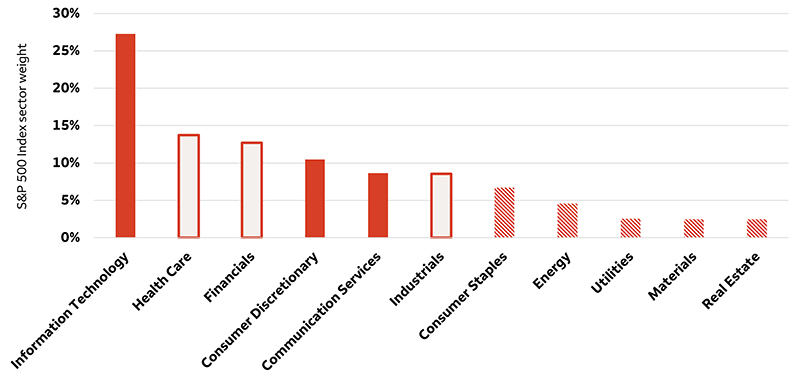
Sources: Bloomberg, McKinsey, and Wells Fargo Investment Institute. Data as of August 18, 2023. Solid bars indicate the sectors most heavily involved in AI development. Outlined bars indicate the sectors that McKinsey studies indicate may stand to benefit most from AI-fueled productivity improvements. Striped bars indicate the sectors that McKinsey studies indicate may benefit to a lesser degree from AI. An index is not managed and not available for direct investment.
Use cases will likely broaden
While most, if not all, sectors and industries will be noticeably altered by the implementation of generative AI, a few stand out. The McKinsey study estimated that industries within the Health Care, Financials, and Industrials sectors could see the greatest value add through AI implementation relative to existing revenues.
Potential generative AI use cases and capabilities by industry
| Industry |
Use cases and capabilities |
| Automotive & transportation |
Self-driving cars, efficient car-sales process, connected vehicles, city of the future, ride sharing, and connected vehicles |
| Health care |
Improved patient data sharing, robotic surgeries, efficient patient/physician care, personalized patient management, diagnosis, accelerated drug discovery and development |
| Consumer goods |
More efficient inventory and labor management, improved marketing and customer service, and supply-chain efficiency |
| Retail/restaurants |
Customer demand tracking, inventory optimization, call center virtual assistants, personalized customer recommendations, automated service, and upsell products at point of service |
| Advertising, sales, & marketing |
Customized advertising campaigns, content creation including generation of graphics and/or images, voice synthesis, and customer-facing chat bots |
| Manufacturing |
More robotics in manufacturing and distribution, supply-chain optimization, efficient warehousing, internet of things, and factory automation |
| Financial services |
High-level financial recommendations, faster data access, improved product development, fraud detection, improved risk management, fintech applications for personal finance and lending, and robo-advisors |
| Technology |
Workflow optimization, generation of code, process automation, and chat bots for customer support |
| Education |
Enhanced digital learning capabilities, enhanced critical thinking from students, increased access to information, copyright/plagiarism detection, higher teacher/student engagement, and personalized tutoring |
| Entertainment |
Music generation, video editing and content creation, and video-game interaction |
Sources: Wells Fargo Investment Institute and McKinsey, 2023.
3 McKinsey & Company, “Economic Potential of Generative AI: The Next Productive Frontier,” June 14, 2023.
The rise of generative AI is similar to the development and advancement of other disruptive technologies — while the technology and infrastructure may be there, broader acceptance and scalability may still be lacking. The technology has the potential to be broadly transformative, but there are many outstanding questions and concerns that need to be addressed before it is widely accepted on a larger scale.
Labor market disruptions
Labor markets are among the areas most exposed to AI’s potentially disruptive effects, in tandem with the potential lift to productivity. Generative AI’s impact on the labor market likely will be more nuanced than more traditional AI systems. Earlier AI systems have been geared more toward automation that jeopardizes jobs in an array of labor-intensive services industries — from food services to office support to the same customer service and sales likely benefiting from more advanced, generative AI. We expect that generative AI’s disruptive effect on the labor market will likely be similar to other forms of automation — as in the past, its impact will likely be mitigated over time by new lines of work created by the innovations themselves.
Government regulation
Governments around the world are becoming increasingly involved in the regulation of AI, based partly on concerns about societal impacts and data privacy. Thus far, initiatives have ranged from industry pledges of voluntary safety guardrails in the deployment of new products to Federal Trade Commission requests for companies’ details related to integration of AI into their operations.
As governments worldwide attempt to regulate AI, we think these efforts need to be balanced and measured appropriately to prevent any potential slowdown in the pace of innovation for generative AI going forward. According to Stanford University’s AI Index, the total number of AI-related bills passed into law has shown a noticeable increase from only one bill passing in 2016 to 37 passing in 2022.
Number of AI bills passed into law (2016 – 2022) 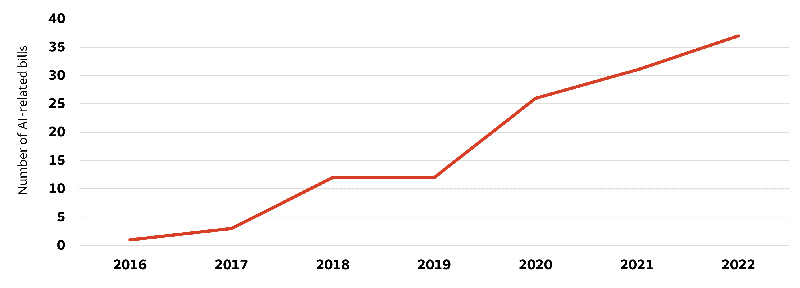
Sources: Wells Fargo Investment Institute and Stanford University Institute for Human-Centered AI, “The AI Index 2023 Annual Report,” April 2023.
Escalating costs and energy requirements
Immediate issues in generative AI implementation include both the computing power and cost of data-intensive model development. At the moment, the costs associated with developing, training, and managing generative AI large language models effectively are fairly prohibitive as these models are very compute-, semiconductor-, networking-, and storage-intensive. The cost for training large language models is quite expensive, although less so for inference, which occurs when the already trained large language model is prompted for a response.
Accuracy concerns
Risks and questions have already surfaced around the outcomes generated by hallucinating large language models. For example, issues have arisen around ChatGPT providing answers with conviction that turn out to be inaccurate. Since the large language models were trained on the structure of language, these models are more focused on the structure of which word or what concept comes next and less focused on whether the answer is accurate.
Geopolitical risks
We have witnessed escalating trade tensions between China and the U.S. since 2018, and this led to a growing number of Chinese companies being added to the U.S. Department of Commerce Entity List. The trade tensions between the U.S. and China have spilled over to the AI market.
In May of 2023, China banned its infrastructure companies from purchasing memory chips from the largest U.S.-based memory-chip manufacturer. Additionally, China imposed export restrictions targeting U.S. semiconductor companies for key semiconductor materials, including gallium- and germanium-based chips. The Biden administration signed an executive order on August 10, 2023 banning new U.S. investment in Chinese companies exposed to AI, semiconductors, and quantum computing.


 Sources: Wells Fargo Investment Institute, Bloomberg, and IDC. Data as of June 1, 2023. E = estimated. Estimates based on Bloomberg Intelligence forecasts using IDC data for the overall generative AI market.
Sources: Wells Fargo Investment Institute, Bloomberg, and IDC. Data as of June 1, 2023. E = estimated. Estimates based on Bloomberg Intelligence forecasts using IDC data for the overall generative AI market.
 Sources: Bloomberg, McKinsey, and Wells Fargo Investment Institute. Data as of August 18, 2023. Solid bars indicate the sectors most heavily involved in AI development. Outlined bars indicate the sectors that McKinsey studies indicate may stand to benefit most from AI-fueled productivity improvements. Striped bars indicate the sectors that McKinsey studies indicate may benefit to a lesser degree from AI. An index is not managed and not available for direct investment.
Sources: Bloomberg, McKinsey, and Wells Fargo Investment Institute. Data as of August 18, 2023. Solid bars indicate the sectors most heavily involved in AI development. Outlined bars indicate the sectors that McKinsey studies indicate may stand to benefit most from AI-fueled productivity improvements. Striped bars indicate the sectors that McKinsey studies indicate may benefit to a lesser degree from AI. An index is not managed and not available for direct investment.
 Sources: Wells Fargo Investment Institute and Stanford University Institute for Human-Centered AI, “The AI Index 2023 Annual Report,” April 2023.
Sources: Wells Fargo Investment Institute and Stanford University Institute for Human-Centered AI, “The AI Index 2023 Annual Report,” April 2023.