Asset allocation and diversification are investment methods used to help manage risk. They do not guarantee investment returns or eliminate risk of loss including in a declining market.
Each asset class has its own risk and return characteristics. The level of risk associated with a particular investment or asset class generally correlates with the level of return the investment or asset class might achieve. Stock markets, especially foreign markets, are volatile. Stock values may fluctuate in response to general economic and market conditions, the prospects of individual companies, and industry sectors. Foreign investing has additional risks including those associated with currency fluctuation, political and economic instability, and different accounting standards. These risks are heightened in emerging markets. Small- and mid-cap stocks are generally more volatile, subject to greater risks and are less liquid than large company stocks. Bonds are subject to market, interest rate, price, credit/default, liquidity, inflation and other risks. Prices tend to be inversely affected by changes in interest rates. High yield (junk) bonds have lower credit ratings and are subject to greater risk of default and greater principal risk. Although Treasuries are considered free from credit risk they are subject to other types of risks. These risks include interest rate risk, which may cause the underlying value of the bond to fluctuate. The commodities markets are considered speculative, carry substantial risks, and have experienced periods of extreme volatility. Investing in a volatile and uncertain commodities market may cause a portfolio to rapidly increase or decrease in value which may result in greater share price volatility. Real estate has special risks including the possible illiquidity of underlying properties, credit risk, interest rate fluctuations and the impact of varied economic conditions.
Sector investing can be more volatile than investments that are broadly diversified over numerous sectors of the economy and will increase a portfolio’s vulnerability to any single economic, political, or regulatory development affecting the sector. This can result in greater price volatility. Communication Services companies are vulnerable to their products and services becoming outdated because of technological advancement and the innovation of competitors. Companies in the Communication Services sector may also be affected by rapid technology changes, pricing competition, large equipment upgrades, substantial capital requirements and government regulation and approval of products and services. In addition, companies within the industry may invest heavily in research and development which is not guaranteed to lead to successful implementation of the proposed product. Risks associated with the Consumer Discretionary sector include, among others, apparel price deflation due to low-cost entries, high inventory levels and pressure from e-commerce players, reduction in traditional advertising dollars, increasing household debt levels that could limit consumer appetite for discretionary purchases, declining consumer acceptance of new product introductions, and geopolitical uncertainty that could affect consumer sentiment. Consumer Staples industries can be significantly affected by competitive pricing particularly with respect to the growth of low-cost emerging market production, government regulation, the performance of the overall economy, interest rates, and consumer confidence. The Energy sector may be adversely affected by changes in worldwide energy prices, exploration, production spending, government regulation, and changes in exchange rates, depletion of natural resources, and risks that arise from extreme weather conditions. Investing in the Financial services companies will subject an investment to adverse economic or regulatory occurrences affecting the sector. Some of the risks associated with investment in the Health Care sector include competition on branded products, sales erosion due to cheaper alternatives, research and development risk, government regulations and government approval of products anticipated to enter the market. There is increased risk investing in the Industrials sector. The industries within the sector can be significantly affected by general market and economic conditions, competition, technological innovation, legislation and government regulations, among other things, all of which can significantly affect a portfolio’s performance. Materials industries can be significantly affected by the volatility of commodity prices, the exchange rate between foreign currency and the dollar, export/import concerns, worldwide competition, procurement and manufacturing and cost containment issues. Real estate investments have special risks, including possible illiquidity of the underlying properties, credit risk, interest rate fluctuations, and the impact of varied economic conditions. Risks associated with the Technology sector include increased competition from domestic and international companies, unexpected changes in demand, regulatory actions, technical problems with key products, and the departure of key members of management. Technology and Internet-related stocks, especially smaller, less-seasoned companies, tend to be more volatile than the overall market. Utilities are sensitive to changes in interest rates, and the securities within the sector can be volatile and may underperform in a slow economy.
Alternative investments, such as hedge funds, private equity/private debt and private real estate funds, are speculative and involve a high degree of risk that is appropriate only for those investors who have the financial sophistication and expertise to evaluate the merits and risks of an investment in a fund and for which the fund does not represent a complete investment program. They entail significant risks that can include losses due to leveraging or other speculative investment practices, lack of liquidity, volatility of returns, restrictions on transferring interests in a fund, potential lack of diversification, absence and/or delay of information regarding valuations and pricing, complex tax structures and delays in tax reporting, less regulation and higher fees than mutual funds. Hedge fund, private equity, private debt and private real estate fund investing involves other material risks including capital loss and the loss of the entire amount invested. A fund's offering documents should be carefully reviewed prior to investing.
Hedge fund strategies, such as Equity Hedge, Event Driven, Macro and Relative Value, may expose investors to the risks associated with the use of short selling, leverage, derivatives and arbitrage methodologies. Short sales involve leverage and theoretically unlimited loss potential since the market price of securities sold short may continuously increase. The use of leverage in a portfolio varies by strategy. Leverage can significantly increase return potential but create greater risk of loss. Derivatives generally have implied leverage which can magnify volatility and may entail other risks such as market, interest rate, credit, counterparty and management risks. Arbitrage strategies expose a fund to the risk that the anticipated arbitrage opportunities will not develop as anticipated, resulting in potentially reduced returns or losses to the fund.
Investing in a direct lending perpetual fund involves significant risks, including the potential loss of principal. These funds typically invest in privately originated loans to corporate borrowers, which may be speculative, illiquid, and subject to limited regulatory oversight. An investment should be considered only by investors who can bear substantial risks and who do not require immediate liquidity. The fund invests primarily in loans to middle-market or non-investment-grade companies. Such borrowers often have higher leverage, limited operating histories, or cyclical business models, increasing the likelihood of: payment delays or defaults, covenant breaches, restructurings or bankruptcies. Losses on individual loans may be significant and could reduce or eliminate investor returns.
Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index is composed of the Bloomberg U.S. Government/Credit Index and the Bloomberg U.S. Mortgage-Backed Securities Index and includes Treasury issues, agency issues, corporate bond issues, and mortgage-backed securities.
Bloomberg Commodity Index is a broadly diversified index of commodity futures on 20 physical commodities, subdivided into energy, U.S. agriculture, livestock, precious metals, and industrial metals sectors. Commodity weights are derived in a manner that attempts to fairly represent the importance of a diversified group of commodities to the world economy.
Cliffwater Direct Lending Index (CDLI) is an asset-weighted, quarterly index measuring the unlevered, gross-of-fees performance of U.S. middle-market corporate loans. It tracks over 20,000 loans held by business development companies (BDCs) through SEC filings.
CDLI-Perpetual (CDLI-P) is comprised primarily of loans held in perpetually structured, non-exchange-traded BDCs and was created to explore the comparative performance of this increasingly popular BDC structure against the entire universe of middle-market loans represented by CDLI.
HFRI Fund Weighted Composite Index is a global, equal-weighted index of over 2000 single-manager funds that report to HFR Database. Constituent funds report monthly net-of-all-fees performance in U.S. dollars and have a minimum of $50 Million under management or a 12-month track record of active performance. The HFRI Fund Weighted Composite Index does not include Funds of Hedge Funds.
IA SBBI U.S. Long-Term Corporate Bond Index is a custom index designed to measure the performance of long-term U.S. investment-grade corporate bonds.
IA SBBI U.S. Long-Term Government Bond Index is a custom index designed to measure the performance of long-term U.S. government bonds.
MSCI EAFE Index (Europe, Australasia, Far East) Index is a free-float-adjusted market-capitalization-weighted index designed to measure the equity market performance of developed markets, excluding the U.S. and Canada.
MSCI Emerging Markets Index is a free-float-adjusted market-capitalization-weighted index designed to measure equity market performance of emerging markets.
Producer Price Index (PPI) is a family of indexes that measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers of goods and services over time.
S&P 500 Index consists of 500 stocks chosen for market size, liquidity, and industry group representation. It is a market-value-weighted index with each stock’s weight in the index proportionate to its market value.
An index is unmanaged and not available for direct investment.
Global Investment Strategy (GIS) is a division of Wells Fargo Investment Institute, Inc. (WFII). WFII is a registered investment adviser and wholly owned subsidiary of Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., a bank affiliate of Wells Fargo & Company.
The information in this report was prepared by Global Investment Strategy. Opinions represent GIS’ opinion as of the date of this report and are for general information purposes only and are not intended to predict or guarantee the future performance of any individual security, market sector or the markets generally. GIS does not undertake to advise you of any change in its opinions or the information contained in this report. Wells Fargo & Company affiliates may issue reports or have opinions that are inconsistent with, and reach different conclusions from, this report.
The information contained herein constitutes general information and is not directed to, designed for, or individually tailored to, any particular investor or potential investor. This report is not intended to be a client-specific suitability or best interest analysis or recommendation, an offer to participate in any investment, or a recommendation to buy, hold or sell securities. Do not use this report as the sole basis for investment decisions. Do not select an asset class or investment product based on performance alone. Consider all relevant information, including your existing portfolio, investment objectives, risk tolerance, liquidity needs and investment time horizon. The material contained herein has been prepared from sources and data we believe to be reliable but we make no guarantee to its accuracy or completeness.
Wells Fargo Advisors is registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, but is not licensed or registered with any financial services regulatory authority outside of the U.S. Non-U.S. residents who maintain U.S.-based financial services account(s) with Wells Fargo Advisors may not be afforded certain protections conferred by legislation and regulations in their country of residence in respect of any investments, investment transactions or communications made with Wells Fargo Advisors.
Wells Fargo Advisors is a trade name used by Wells Fargo Clearing Services, LLC and Wells Fargo Advisors Financial Network, LLC, Members SIPC, separate registered broker-dealers and non-bank affiliates of Wells Fargo & Company.

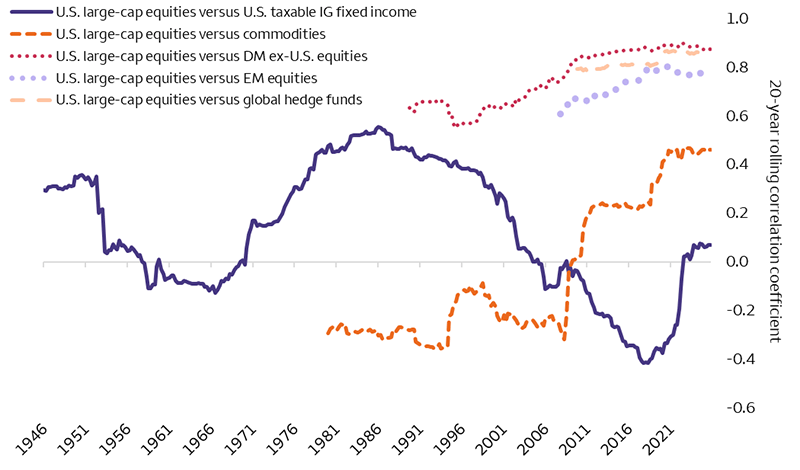 Sources: © Morningstar Direct, All Rights Reserved,1 and Wells Fargo Investment Institute. Quarterly data from January 1, 1946, to December 31, 2025. IG = investment grade. Correlation measures the degree to which asset classes move in sync; it does not measure the magnitude of that movement. There is no guarantee that future correlations between the Indexes will remain the same. U.S. Large Cap Equities: S&P 500 Index. U.S. Taxable Investment Grade Fixed Income: Blend of IA SBBI U.S. Long-Term Government Bond Index and IA SBBI U.S. Long-Term Corporate Bond Index until 1976, and then the Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index. Commodities: Bloomberg Commodity Index. Developed Market ex. U.S. equities: MSCI EAFE Index (Europe, Australasia, Far East) Index. Emerging Market Equities: MSCI Emerging Markets Index. Global Hedge Funds: HFRI Hedge Fund Weighted Composite Index. Index returns do not represent investment performance or the results of actual trading. Index returns reflect general market results, assume the reinvestment of dividends and other distributions, and do not reflect deduction for fees, expenses or taxes applicable to an actual investment. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Correlation measures the degree to which asset classes move in sync; it does not measure the magnitude of that movement. The risk associated with the representative asset classes and the definitions of the indexes are provided at the end of report.
Sources: © Morningstar Direct, All Rights Reserved,1 and Wells Fargo Investment Institute. Quarterly data from January 1, 1946, to December 31, 2025. IG = investment grade. Correlation measures the degree to which asset classes move in sync; it does not measure the magnitude of that movement. There is no guarantee that future correlations between the Indexes will remain the same. U.S. Large Cap Equities: S&P 500 Index. U.S. Taxable Investment Grade Fixed Income: Blend of IA SBBI U.S. Long-Term Government Bond Index and IA SBBI U.S. Long-Term Corporate Bond Index until 1976, and then the Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index. Commodities: Bloomberg Commodity Index. Developed Market ex. U.S. equities: MSCI EAFE Index (Europe, Australasia, Far East) Index. Emerging Market Equities: MSCI Emerging Markets Index. Global Hedge Funds: HFRI Hedge Fund Weighted Composite Index. Index returns do not represent investment performance or the results of actual trading. Index returns reflect general market results, assume the reinvestment of dividends and other distributions, and do not reflect deduction for fees, expenses or taxes applicable to an actual investment. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Correlation measures the degree to which asset classes move in sync; it does not measure the magnitude of that movement. The risk associated with the representative asset classes and the definitions of the indexes are provided at the end of report.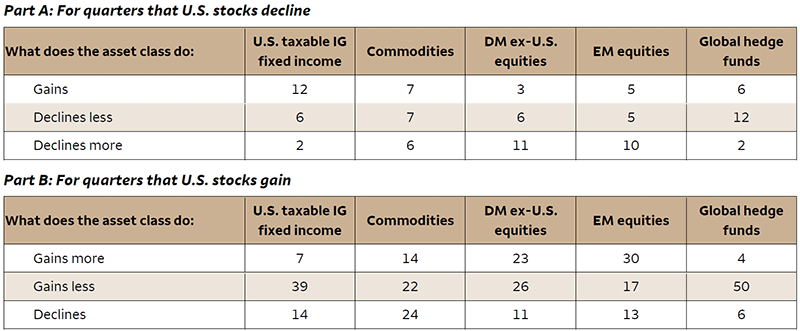
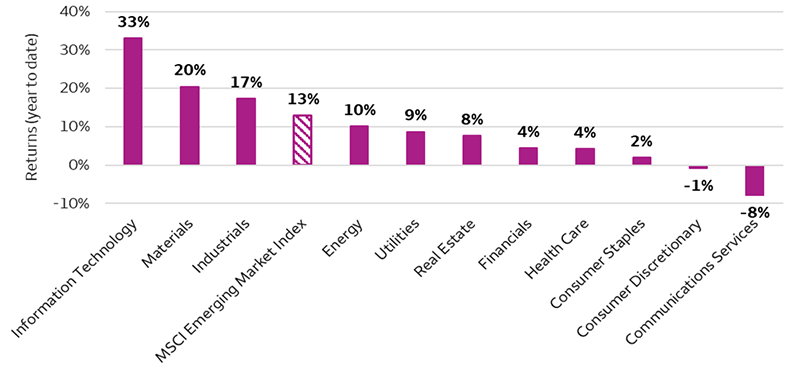 Sources: Bloomberg and Wells Fargo Investment Institute. Daily data is from December 31, 2025 – March 2, 2026. Past performance does not guarantee future results. An index is unmanaged and not available for direct investment.
Sources: Bloomberg and Wells Fargo Investment Institute. Daily data is from December 31, 2025 – March 2, 2026. Past performance does not guarantee future results. An index is unmanaged and not available for direct investment.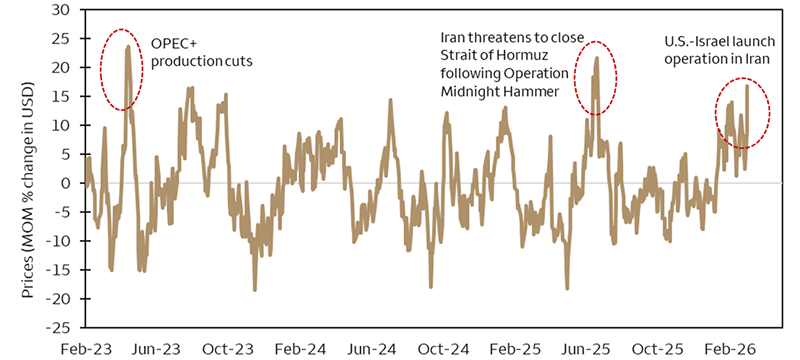 Source: Bloomberg crude oil futures (WTI). Data as of March 3, 2026. MOM = month over month. USD = U.S. dollar.
Source: Bloomberg crude oil futures (WTI). Data as of March 3, 2026. MOM = month over month. USD = U.S. dollar.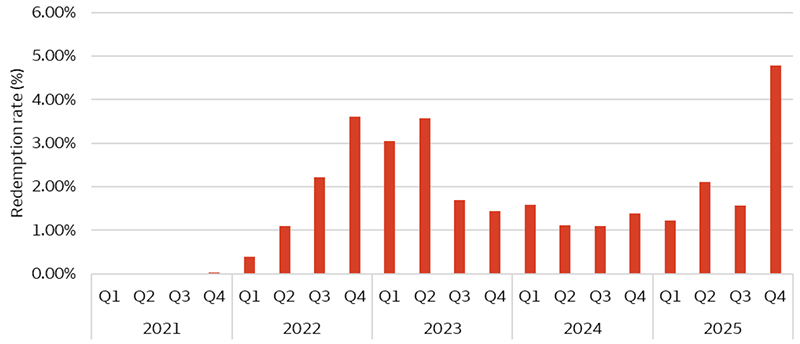 Sources: Cliffwater, Wells Fargo Investment Institute. Data as of December 31, 2025. The data is based on Cliffwater Direct Lending Index – Perpetual. See disclosure for definitions.
Sources: Cliffwater, Wells Fargo Investment Institute. Data as of December 31, 2025. The data is based on Cliffwater Direct Lending Index – Perpetual. See disclosure for definitions.